Photorespiration or C2 cycle
Photorespiration or C2 cycle
In animals and bacteria, only one kind of respiration known as dark respiration occurs.
This is not affected by the presence or absence of light.
But in certain green plants, there are two distinct types of respiration – photorespiration and dark respiration.
Respiration that occurs in photosynthetic tissues in the presence of light and results in increased rate of carbondioxide evolution is called photorespiration or light respiration.
Photorespiration involves three organelles – chloroplasts, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
Oxidation of RuBP in the presence of high oxygen is the first reaction of photorespiration.
This reaction is catalysed by Rubisco* enzyme called carboxylase.
It leads to the formation of 2C compound – phosphoglycolic acid and 3C compound PGA.
When PGA is used up in the Calvin cycle, the phosphoglycolic acid is dephosphorylated to form glycolic acid in the chloroplasts.
From the chloroplast, the glycolic acid diffuses into the peroxisome where it is oxidised to glyoxalic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
In peroxisome from glyoxalic acid, glycine is formed.
Note : * Rubisco = Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase

Glycine molecules enter into mitochondria where two molecules of glycine combine to give a molecule of serine, NH3 and CO2.
During this process, NAD+ is reduced to NADH2.
The aminoacid serine is taken to peroxisome where, it is converted into hydroxy pyruvic acid.
Hydroxy pyruvic acid is reduced by NADH2 to form glyceric acid.
The glyceric acid leaves peroxisome and enters chloroplast, where it is phosphorylated to PGA, which enters into Calvin cycle.
During the photorespiratory pathway, one CO2 molecule released in mitochondria is to be re-fixed.
Photorespiration is also known as photosynthetic carbon oxidation cycle or C2 cycle.
Under the conditions of high light and limited CO2 supply, photo respiration protects the plants from photooxidative damage.
This means that, if enough CO2 is not available to utilize light energy, excess energy causes damage to plant.
However, photo respiration utilizes part of the light energy and saves the plant from photooxidative damage.
Increased O2 level increases photo – respiration whereas increased CO2 level decreases photorespiration and increases photosynthesis.
Difference between photorespiration and dark respiration

For more details about c2 cycle click here
Other links
Plant tissue culture – origin and techniques
Plant physiology – photosynthesis and its significance
Site of photosynthesis and Mechanism of photosynthesis
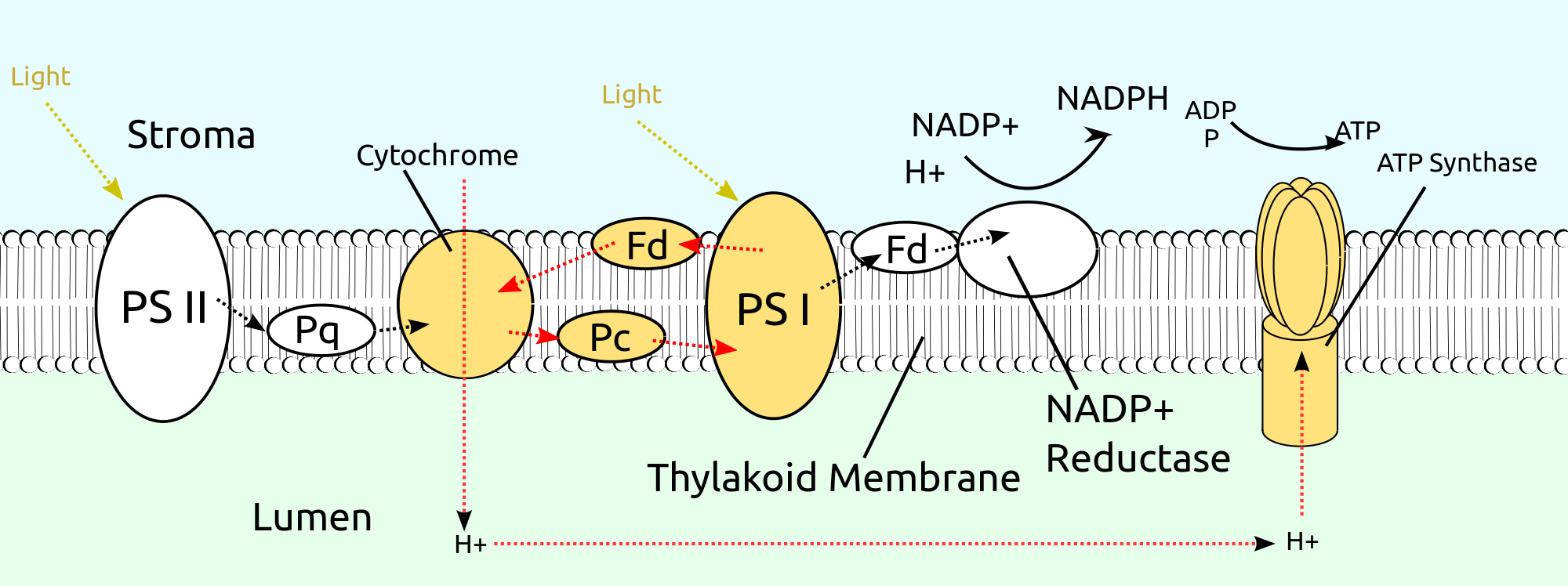
Electron transport system and photophosphorylation types
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Test tube and funnel experiment, Ganong’s light screen experiment
Mode of nutrition – Autotrophic, Heterotrophic
Mechanism of Respiration – Glycolysis
Mechanism of Respiration – Oxidative decarboxylation , Krebs cycle
Mechanism of Respiration – Electron Transport Chain, Energy Yield
Ganong’s respiroscope, Pentose phosphate pathway
Plant growth and Measurement of plant growth
Phytohormones Cytokinin, Ethylene, Abscisic Acid, Growth Inhibitors – Physiological Effects
Photoperiodism and vernalization, Phytochromes and flowering