ME3493 Manufacturing Technology Important Questions
Unit 1
- What are the advantages of using cutting fluids during machining? What are the basic requirements of cutting fluids? Name some of the commonly used types of cutting fluids.
- Differentiate between oblique and orthogonal cutting with suitable schematic diagrams. Also write a note on types of chips produced during oblique cutting.
- List and illustrate the major material properties required of cutting tool.
- Explain what is meant by the term machinability and what it involves. Why does titanium have poor machinability?
- Describe effect of temperature on tool life.
- Explain why continuous chips are not necessarily desirable.
- Comment on the role and importance of the relief angle.
- Explain in detail the following:
(i) Formation of different types of chips.
(ii) Types of cutting fluids. - Describe with neat sketches for force relationship in orthogonal cutting.
Unit 2
- Draw tool and workpiece geometry during turning operation. Mark all cutting forces. Describe how different factors influences cutting forces in turning operations.
If a 125 mm long, 10 mm diameter 304 stainless steel rod is being reduced in diameter to 9 mm by turning on a lathe. The spindle rotates at 360 rpm, and tool is travelling at an axial speed of 1.75 mm/min. Calculate the cutting time required to complete the machining. If specific energy required during machining stainless-steel is 4 W-s/mm³, calculate the power dissipated during machining. - List the types of machining operations that can be performed on a lathe. (5)
- Locate compound rest on lathe machine with sketch. (4)
- Briefly discuss about compound rest and cross slide.
- Give a sketch illustrating the principle of operation of the Swiss-type automatic screw machine and brief their advantages and limitations.
- Draw neat sketches and explain any four work-holding devices in the lathe.
- Estimate the machining time required to rough turn a 0.50-m-long annealed copper-alloy round bar from a 60-mm diameter to a 58-mm diameter, using a high-speed steel tool. Estimate the time required for an uncoated carbide tool. (6)
- A high-strength cast-iron bar 200 mm in diameter is being turned on a lathe at a depth of cut d = 1.25 mm. The lathe is equipped with a 12-kW electric motor and has a mechanical efficiency of 80%. The spindle speed is 500 rpm. Estimate the maximum feed that can be used before the lathe begins to stall?
Unit 3
- Grinding wheel characteristics or the performance of a grinding wheel depends on type of abrasive, grain size, grade, structure and bonding materials. Discuss the effect of each. Also select proper grinding wheel for cylindrical grinding of cast iron work piece.
- Draw the schematic representation of milling cutter, mark all necessary parts and angles. Also draw axis coordinate system for vertical and horizontal milling centres. Identify basic parts of milling machines.
- Explain why milling is such a versatile machining operation.
- Describe the different types of cutters used in milling operations and give an application of each type. (9)
- Explain why the axis of a hob is tilted with respect to the axis of the gear blank. (6)
- A single-thread hob is used to cut 40 teeth on a spur gear. The cutting speed is 35 m/min and the hob is 75 mm in diameter. calculate the rotational speed of the spur gear.
- Describe with neat sketches, the quick return mechanism of a shaper. (9)
- Differentiate the up-milling from down-milling process.
- Discuss the three types of feed in a centreless grinding machine.
- Explain wheel truing and dressing.
Unit 4
- Identify the differences between mechanization and automation.
- Define numerical control machines with example.
- Discuss the following CNC control systems with a neat sketch.
(i) Closed loop system and open loop system.
(ii) Straight-line system
(iii) Continuous system - Define constructional features of CNC machine tools.
- Explain open-loop and closed-loop control circuits with sketch.
- Describe the factors that have led to the development of numerical control.
- What are the basic components of NC system? Discuss with the help of their functions. With neat diagram differentiate between open and close loop control system, point-to-point and continuous positioning systems in CNC machines.
- List out the basic CNC machine elements, discuss their functions. Also write a note on interpolation methods and their applications.
Unit 5
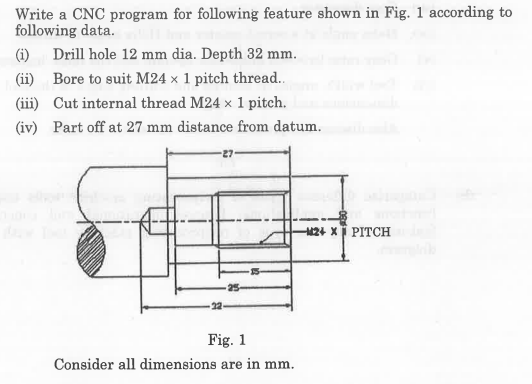
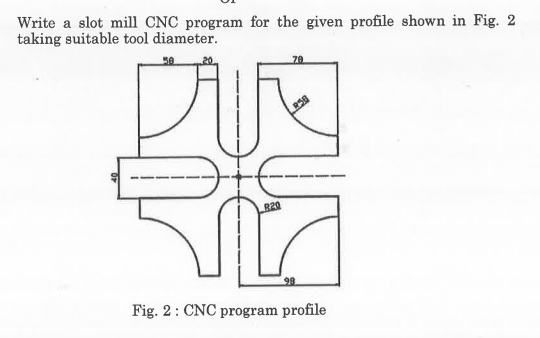
- Define significance of computer-integrated manufacturing operations.
- Explain with flow chart of setting up a CNC machine for machining in lathe.
- Define terms fixed cycles, loops and subroutine in computer numerical control machine.
- Differentiate the terms computer aided and computer integrated.
- Describe manual part programming with examples.
- Explain in detail the following:
(i) Interpolators and their types.
(ii) Absolute and incremental coordinate systems.